World Beef Trade
Author
Published
11/5/2025
The United States is a major player in the world beef market. Even with a persistent decline in the cattle herd over time, the United States is once again expected to be the world’s top producer and consumer of beef and veal, closely followed by Brazil and China.
When it comes to global beef trade, the United States remains in the top 5 for exports and imports of beef and veal. The United States ranks seconds in volume of beef imports (2.2 million mt), behind only China. Brazil remains the world’s largest exporter of beef (3.75 million mt), where the United States ranks fourth (1.2 million mt), trailing behind Australia and India who are the world’s second and third largest exporters of beef, respectively.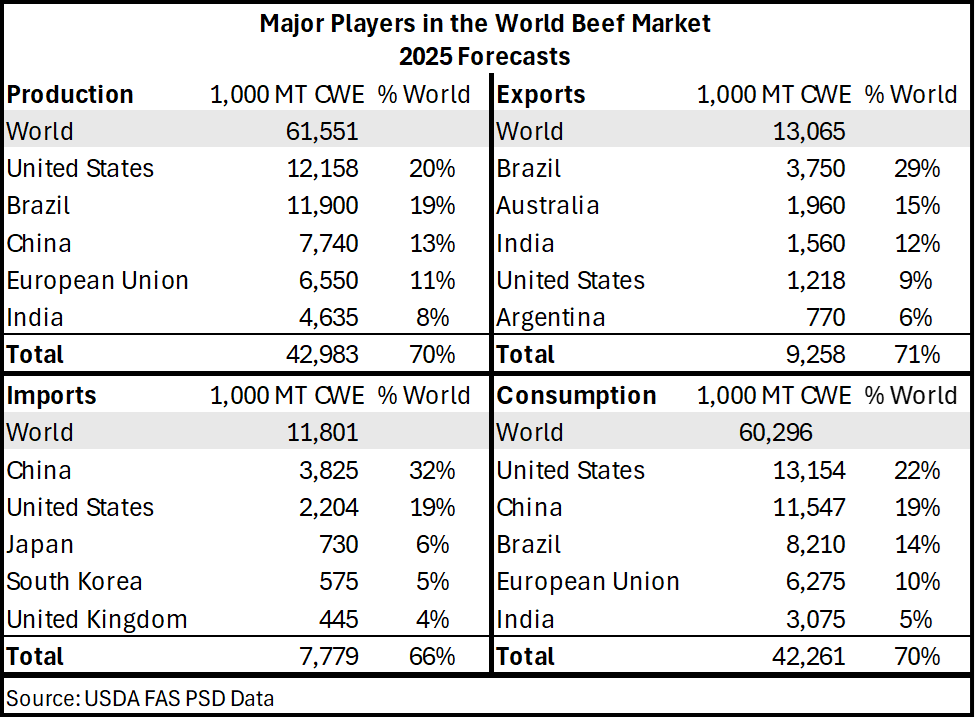 Table 1. Major Countries in the World Beef Market
Table 1. Major Countries in the World Beef Market
Relative Value of U.S. Beef Imports and Exports
To get a more detailed look into world beef trade, the rest of this article utilizes UN Comtrade data, a detailed monthly trade database. Data utilized from UN Comtrade is not directly comparable to Table 1, but the data tells a similar story.
Typically, the United States imports and exports approximately the same amount of beef in terms of volume. Figure 1 illustrates U.S. beef exports and imports by value; Figure 2 shows U.S. beef export and import by volume; and Figure 3 illustrates the average price of a metric ton of traded beef. With the exception of a few years in the early 2000s when the United States imported more beef in terms of volume and value, the volume of beef exports and imports remain roughly the same.
In terms of total value, exports are typically higher than imports; however, at this point in 2025, the value of exports and imports are both declining while the current average price of imports is nearly 6% higher than 2024. Note that Figures 1-3 only account for beef exports and imports from January through September 2025.
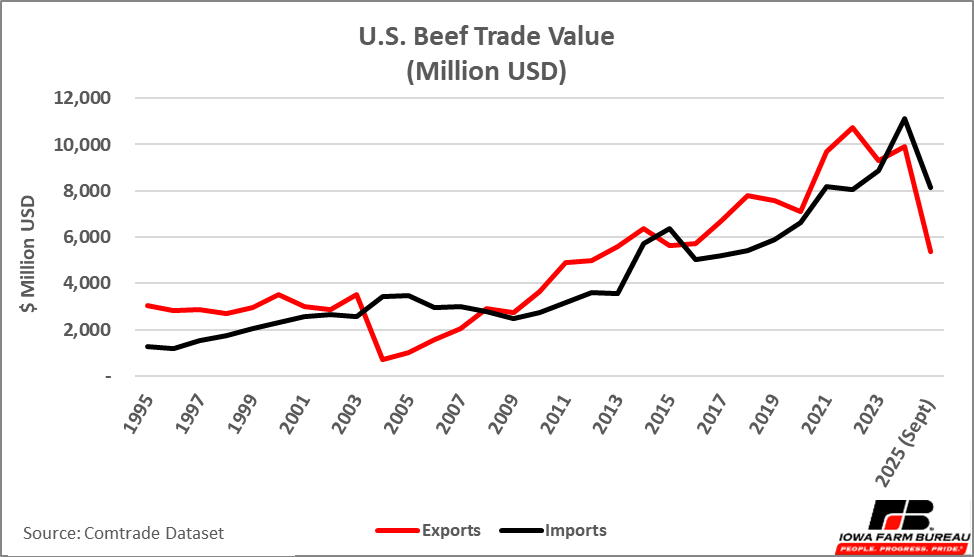 Figure 1. Value of U.S. Beef Exports and Imports 1997-Sept. 2025
Figure 1. Value of U.S. Beef Exports and Imports 1997-Sept. 2025
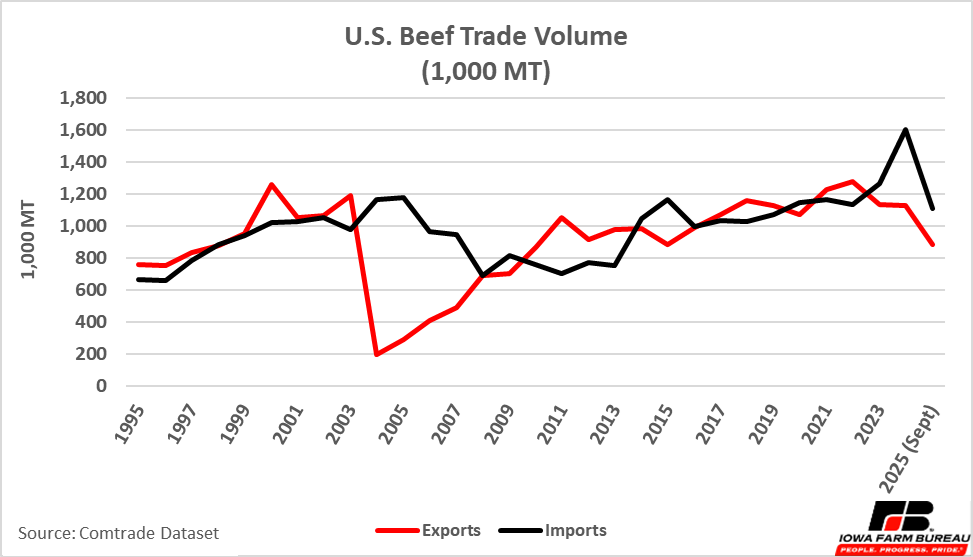 Figure 2. Volume of U.S. Beef Exports and Imports 1997-Sept. 2025
Figure 2. Volume of U.S. Beef Exports and Imports 1997-Sept. 2025
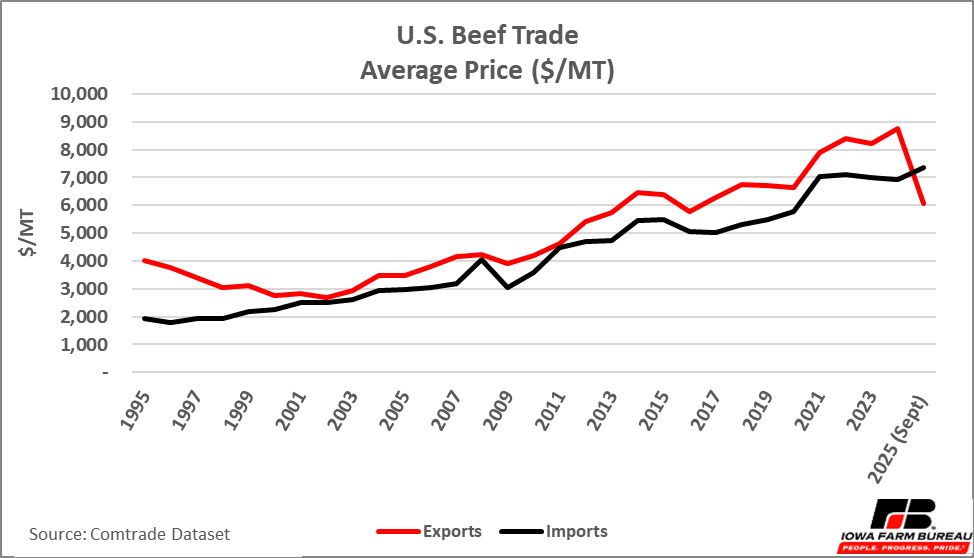 Figure 3. Average Price of U.S. Beef Exports and Imports 1997-Sept. 2025
Figure 3. Average Price of U.S. Beef Exports and Imports 1997-Sept. 2025Major Trade Partners for U.S. Beef
As we enter the final quarter of 2025, South Korea and China remain the largest buyers of United States beef, together accounting for almost half (47%) of all United States beef exports. Australia, New Zealand, and Mexico continue to be the primary suppliers of foreign beef to the United States (Table 2). Imported beef is generally lower-value cuts, often used for ground beef, whereas the United States tend to include higher-value cuts.
Although Table 2 presents the five-year average and excludes 2025 data, trade data from the first three quarters of 2025 indicate that these trends are holding steady as we round out the year. To date, United States beef exports total approximately 886,340 MT, with South Korea (234.7 thousand MT) and Japan (148.4 thousand MT) remaining the top two destinations of United States beef exports. Similarly, United States beef imports through the same period total approximately 1.1 million MT led by Australia (254.6 thousand MT) and Canada (198.6 thousand MT).
As the year concludes, the United States continues to see similar trends in its leading beef trade partners for both exports and imports.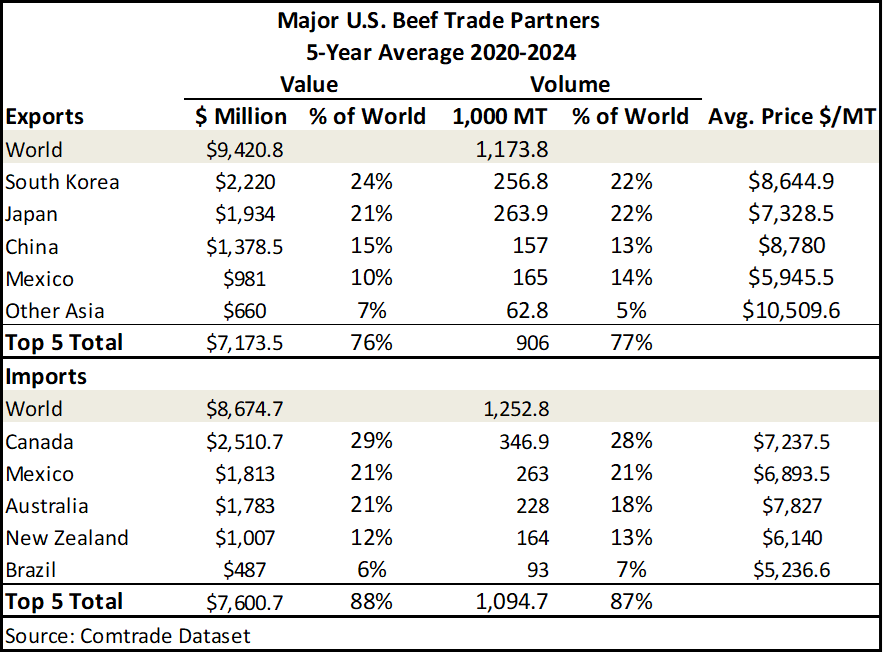 Table 2. Major U.S. Beef Trade Partners
Table 2. Major U.S. Beef Trade PartnersA recent announcement by President Trump proposed the idea of importing beef from Argentina in an effort to lower beef prices for consumers. Argentina ranks below the United States in terms of beef exports, exporting an estimated 807.8 thousand MT ($3.1 million USD) in 2024 compared to 1.13 million MT ($9.9 billion USD) exported by the United States in 2024. Not ranking as a top beef trade partner for the United States, Argentina has exported a total 124.2 thousand MT to the United States over the last five years, valued at an estimated $697 million USD making the United States a top beef trade partner in terms of quantity, but not value.
Markets of Other Major Importers and Exporters
While the United States plays a dominant role in the global beef market, countries like Brazil, Australia, India, and Netherlands also play a major role in the global beef export market (Table 3). While data in Table 3 is a five-year average and excludes 2025 data, data from the first three quarters of 2025 tell us that we will likely continue to see a similar trend as the year comes to an end. At this point in 2025, Brazil has exported an estimated 2.3 million MT of beef, up 8% from the five-year average in Table 3.
China continues on as the world’s largest importer of beef with their primary suppliers being Brazil and Argentina. The United States is not one of the top five suppliers of Chinese beef, but China is the third largest export market for U.S. beef. Japan and South Korea are also other major importers of beef. While the data in Table 4 excludes data from 2025, at this point in the year, Japan as the second largest importer of beef, has imported 361.4 thousand MT of beef. This is nearly 41% down from 2024 totals.India has surpassed the United States to become the world’s third largest beef exporter. A substantial portion of India’s beef production and exports are derived from water buffalo (mostly carabeef). As Table 3 highlights, a majority of India’s top export destinations are Asian countries and are not top-ranking beef importing countries.
China remains the world’s largest importer of beef, importing, on average, 2.3 billion MT every year over the last five years. Its primary suppliers are Brazil and Argentina, who account for well over half of their imports on a volume and value basis. China’s top five beef suppliers account for 90% of their total beef imports, which does not include the United States. The United States is the sixth largest supplier of beef to China, but accounts for only 3% of China’s total beef imports. New Zealand and Uruguay account for 9% and 11%, respectively.
Germany, though a top import destination in the global market for beef, sources a significant majority of its beef imports from within the European Union. The EU imports a majority of their beef from major producers in South America (Argentina and Brazil) and the United Kingdom.
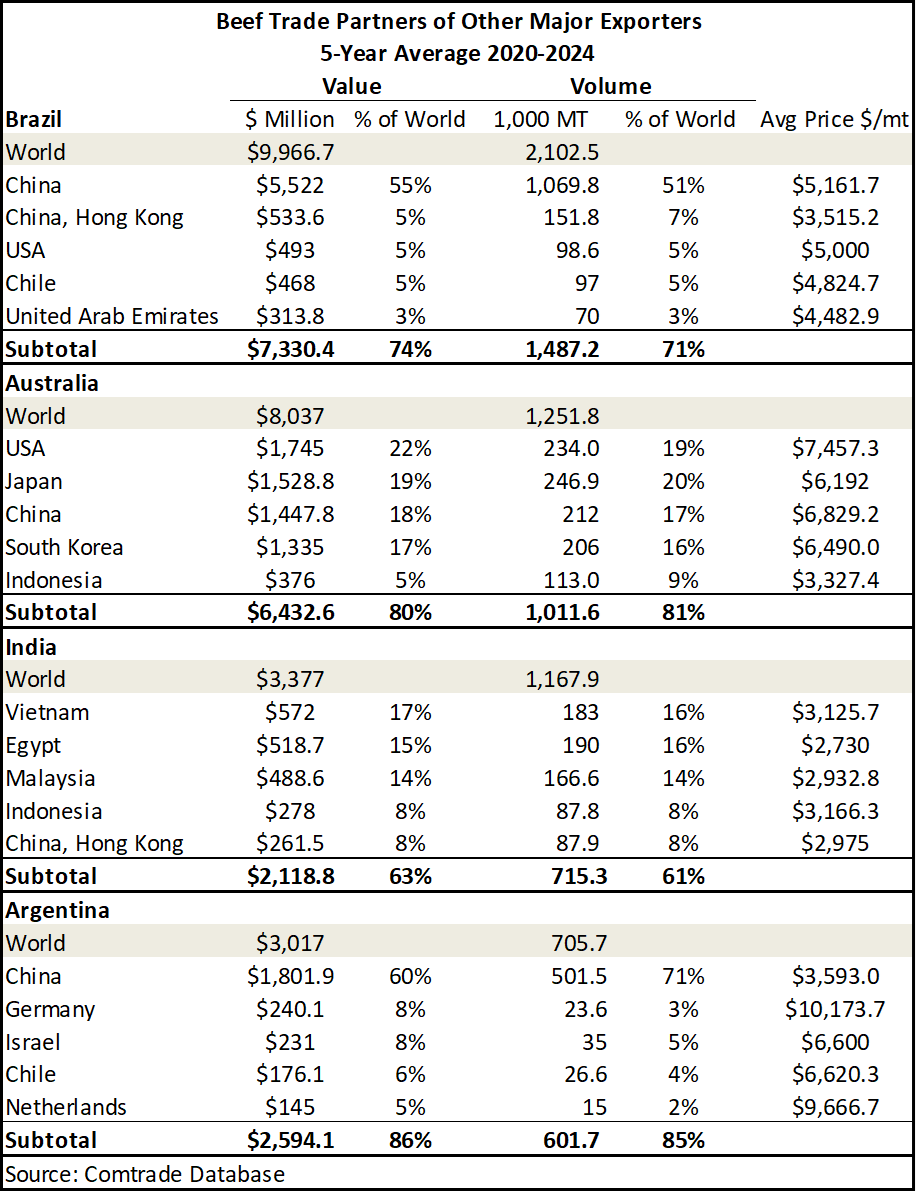 Table 3. Trade Partners of Major Exporters other than The United States
Table 3. Trade Partners of Major Exporters other than The United States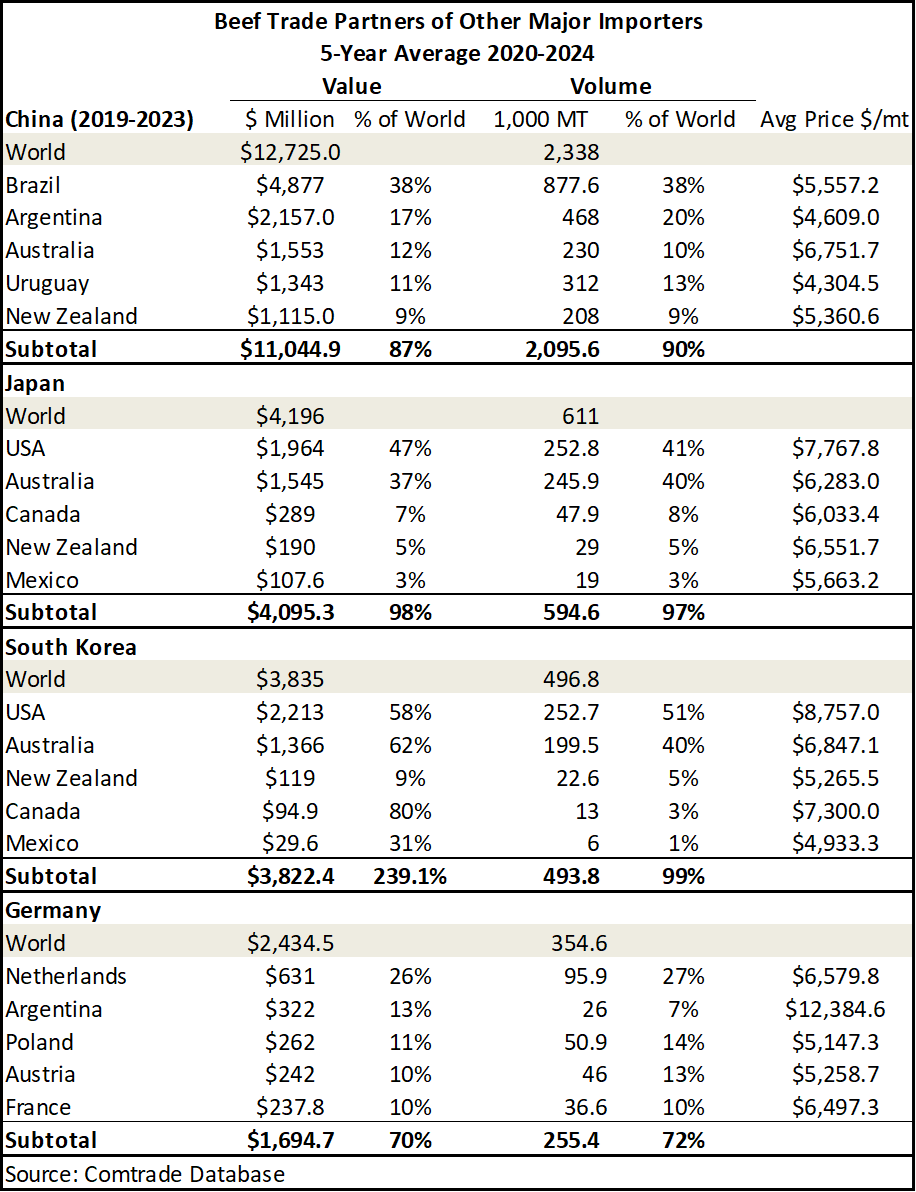 Table 4. Trade Partners of Major Importers Other than The United States
Table 4. Trade Partners of Major Importers Other than The United StatesEconomic analysis provided by Paige Klipstein, Research Analyst, Decision Innovation Solutions, on behalf of Iowa Farm Bureau
Want more news on this topic? Farm Bureau members may subscribe for a free email news service, featuring the farm and rural topics that interest them most!