U.K. Joining the Comprehensive Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership
Author
Published
6/6/2023
NOTE: Iowa Farm Bureau will be taking 22 members and staff to the U.K. in June for its annual Market Study Tour. The goal of the trip is to get a better understanding of the impacts of Brexit on U.S., U.K., and E.U. trade and relationships. Please contact Stacy Stevens at sstevens@ifbf.org for information regarding applying for future market study tours.
On March 31, 2023, the United Kingdom (U.K.) announced the conclusion of negotiations on the accession of the U.K. to the free trade agreement Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP). This free trade agreement was signed on March 8, 2018, among 11 countries: Australia, Brunei, Canada, Chile, Japan, Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Peru, Singapore, and Vietnam. The conclusion of negotiations indicates the U.K. and CPTPP negotiations teams have jointly decided as of March 31, 2023, what should be included in the agreement once it is finished. The teams now have initiated the process to prepare the documents for signature.
According to U.K. Department for Environment Food & Rural Affairs[1], the CPTPP will benefit the country by cutting tariffs on goods exports, expanding opportunities from diversifying supply chains, accessing new markets for U.K. service providers, enhancing data flows, allowing a trade deal with Malaysia for the first time, improving access to high-quality consumer goods, strengthening economic security, and fostering investment.
Table 1. U.K. Total Trade of Good & Services by Country (2021Q4-2022Q3)
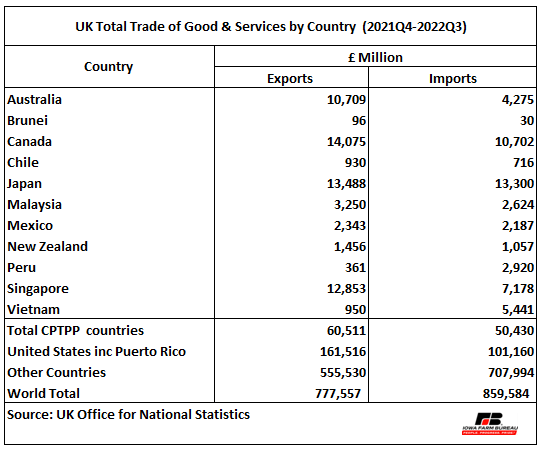
Data from the U.K. Office for National Statistics indicates that from October 2021 to September 2022, the U.K. export of good and services to CPTPP countries were estimated at £60.5 billion ($75.2 billion USD), which represented 7.8% of total U.K. exports. At the same time, imports from those countries were worth £50.4 billion ($62.7 billion USD), which made up 5.9% of total imports (see Table 1). The Conclusion of Negotiations document[2] highlighted that 99% of exports to CPTPP would be eligible for zero tariffs, including cars and machinery. Dairy products, such as cheese and butter, will benefit with lower tariffs in Canada, Japan, and Mexico. Exports of chocolate to Mexico and Malaysia will have zero tariffs.
Table 2 shows how the U.K. has agreed to proportionate market access for sensitive agricultural commodities including beef, pork, chicken, sheep meat, and eggs from CPTPP countries. The access varies by country and commodities and includes a combination of duty free and tariff-rate quotas (TRQ).
Table 2. U.K. Agreement in Terms of Proportionate Market Access for Sensitive Agricultural Goods from CPTPP Members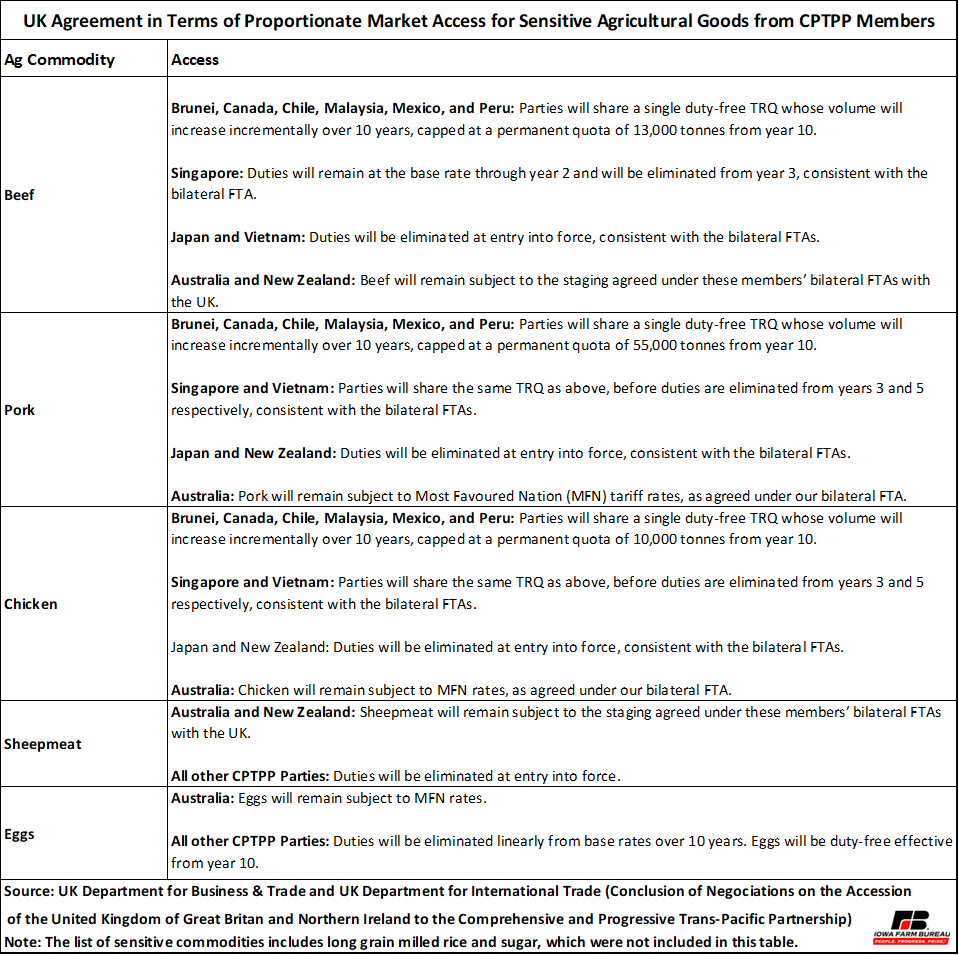
In the long run, by joining the CPTPP, the U.K. could add about £1.7 billion ($2.1 billion USD) in exports to the other members of the CPTPP (see footnote 2). As a reference, taking the value of U.K. exports of goods and services to CPTPP members during the four quarters from October 2021 to September 2022 as a baseline (£60.5 billion), this free trade agreement would increase exports to the CPTPP members by 2.8% in the long run. Also, from the total value of U.K. exports during the same period (£777.58 billion), the increase in U.K. total exports would be about 0.22% in the long run.
U.S. agricultural exports to TPP 11 members made up 41.6% ($81.6 billion USD) of total U.S. agricultural exports in 2022. The large share is because TPP members include Mexico, Canada, and Japan, which after China, are the top 2, 3, and 4 market destinations for the U.S. agricultural commodities. Without these 3 countries, exports to the TPP members represented 5.2% ($10.2 billion USD) of total U.S. agricultural exports in 2022.
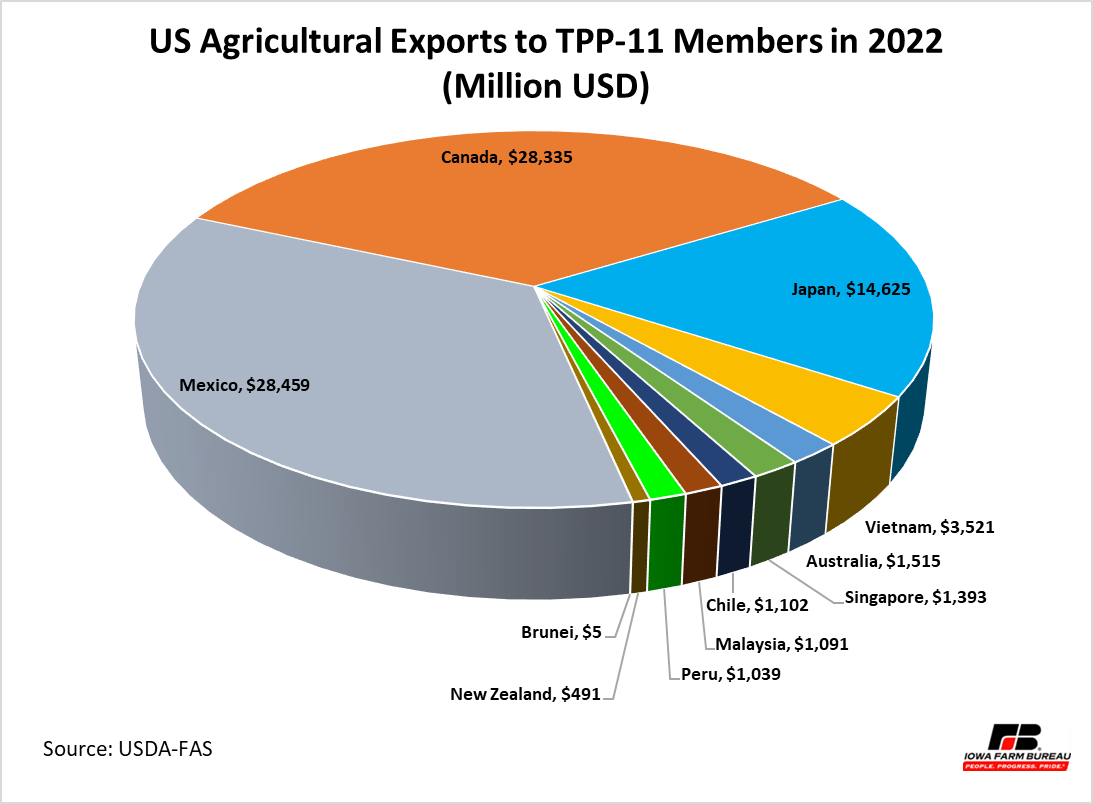
Figure 1. US Agricultural Exports to TPP Members in 2022 (Million USD)
Although the U.S. is not a signatory of the CPTTP, according to the Office of the United States Trade Representative, the U.S. has comprehensive free trade agreements with six of the CPTTP members (Australia, Canada, Chile, Mexico, Peru, and Singapore). In addition, the U.S. has an agreement concentrating on free trade in critical minerals with Japan.
Want more news on this topic? Farm Bureau members may subscribe for a free email news service, featuring the farm and rural topics that interest them most!